
Drug Target Models
GPCR Reporter Cells
Immunotherapy cells
Other Stable Cells
Assay Kits & Reagents
Services
Resources
Company
Professional technology integration to support the entire R&D process
Plasmid Electroporation
Product Description
Cycle Pricing
Case Studies
Definition
Electroporation, also known as electropermeabilization, is a highly efficient non-viral delivery method for introducing nucleic acids (DNA or RNA), proteins, drugs, and other molecules into cells. Short, controlled electrical pulses transiently permeabilize the cell membrane, enabling the uptake of these molecules.
Following electroporation, plasmid DNA may remain episomal (non-integrated) or, depending on the experimental design, integrate into the host genome, resulting in transient or stable expression.
Working principle
During in vitro electroporation, a suspension of target cells and the plasmid DNA to be introduced into the cells are mixed in a conductive solution and placed in a cuvette (Figure 1). The sample chamber of the electroporation cuvette has two metal plates on either side, allowing an electric current to pass through the mixture. The cuvette is placed in the chamber of the electroporator, which is equipped with appropriate electrical contacts to complete the circuit. The controller on the electroporator allows the user to set the voltage, waveform, and duration of the delivered electrical pulse. These parameters are optimized according to the specific cell type to achieve efficient delivery while maintaining cell viability.
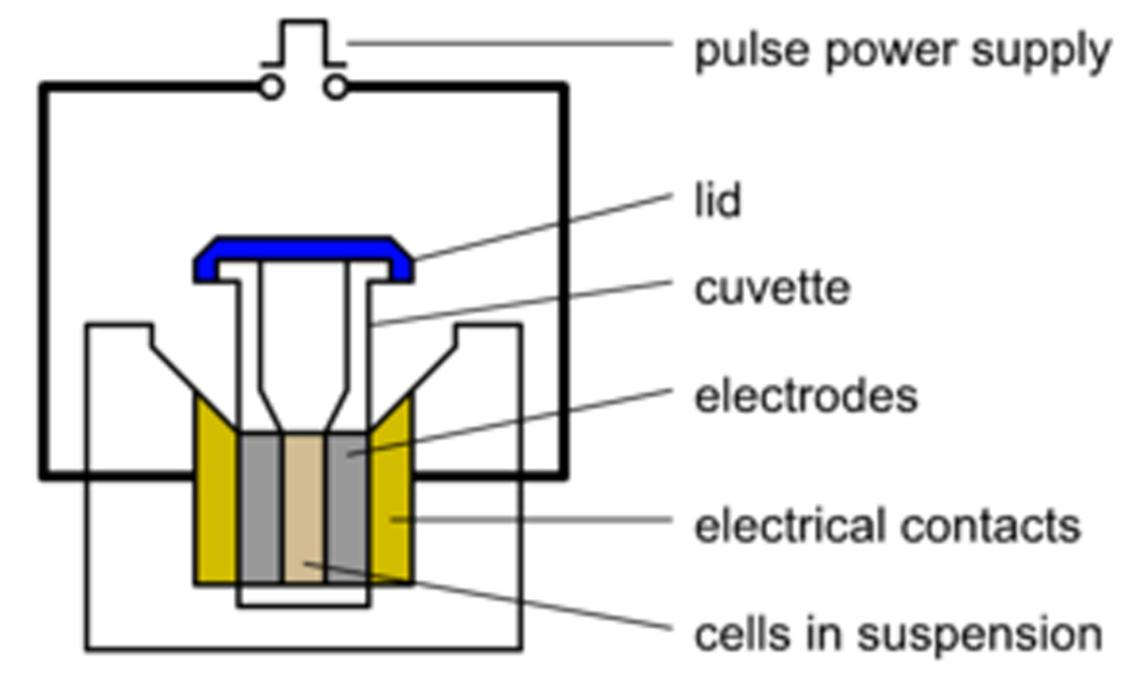
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the main components of an electroporator with a cuvette. Image credit: Richard Wheeler
An electrical pulse disrupts the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane, forming pores (Figure 2). This process is asymmetric, with pores initially forming on the anodic side of the cell. Simultaneously, the transmembrane potential increases. This forces charged molecules (such as plasmid DNA) to initially adhere to the membrane on the cathodic side of the cell and then pass through these pores into the cell (Figure 3).
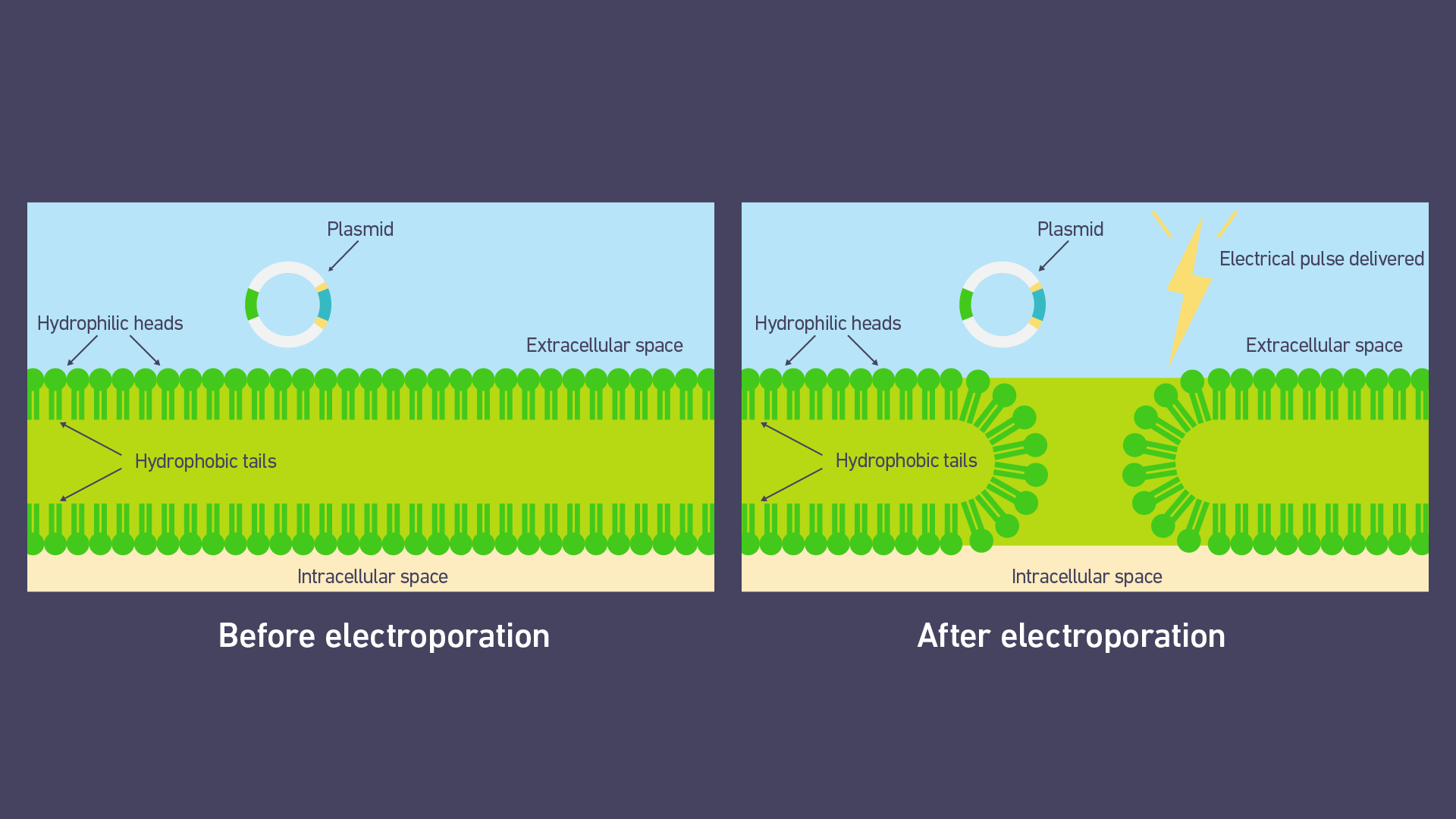
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of cell membrane disruption and pore formation during electroporation. Image source: Technology Networks.
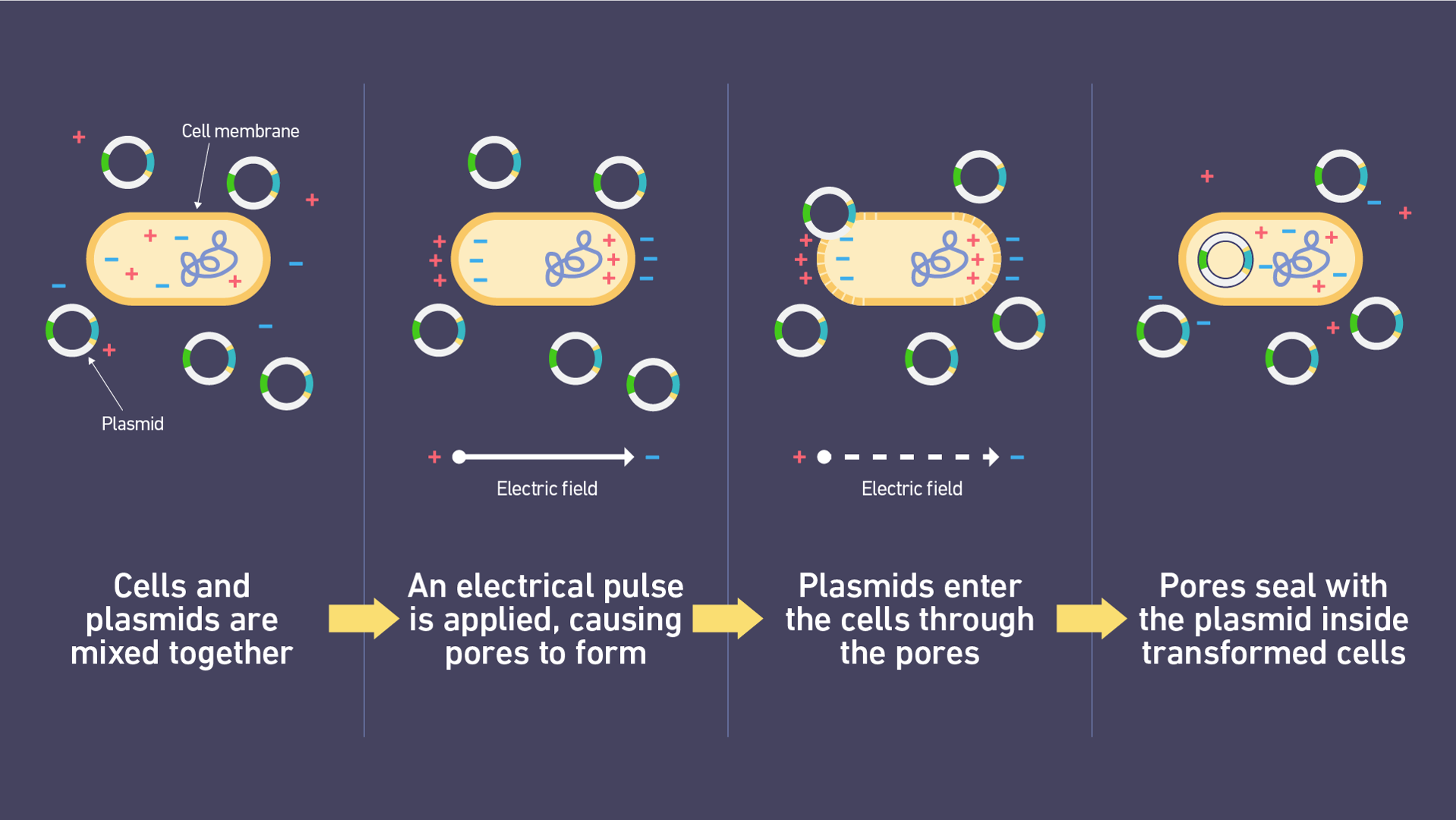
Figure 3: Schematic diagram showing the steps and associated charges during electroporation to introduce foreign material (in this case, a plasmid) into cells. Image source: Technology Networks.
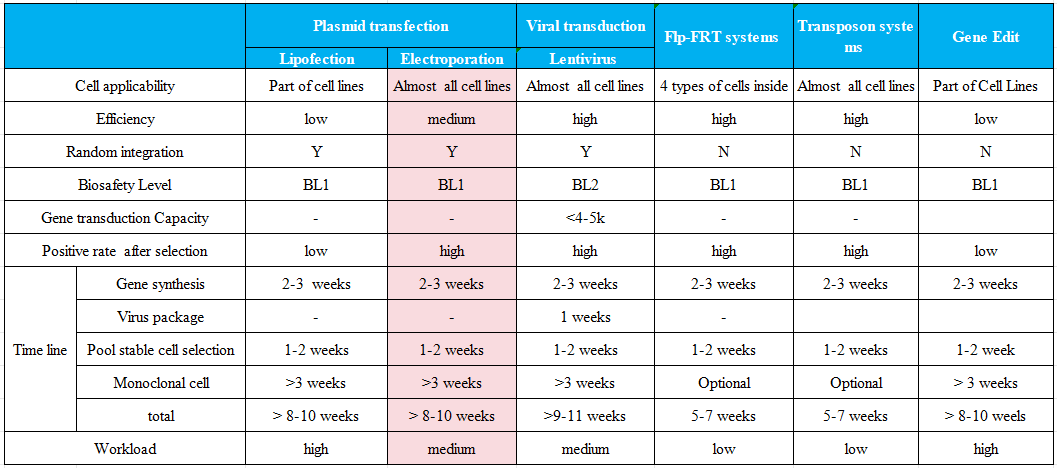
Service advantages and limitations

Key Parameters
When developing an electroporation protocol, it is crucial to select appropriate parameters that achieve permeabilization while minimizing disruption of the cell membrane, thereby maximizing cell viability, experimental reproducibility, and efficiency. Factors to consider include:
1. Waveform: Exponentially decaying pulse vs. square wave pulse
A square wave pulse rapidly rises to a set voltage, maintains that voltage, and then rapidly cuts off at the end of the pulse; an exponentially decaying pulse rapidly rises to the target voltage and then decreases over time. Generally, square wave pulses are preferred for mammalian transfection.
A square wave pulse rapidly rises to a set voltage, maintains that voltage, and then rapidly cuts off at the end of the pulse; an exponentially decaying pulse rapidly rises to the target voltage and then decreases over time. Generally, square wave pulses are preferred for mammalian transfection.
2. Pulse duration: For square wave pulses, the duration is typically set directly; for exponentially decaying pulses, the voltage gradually decreases over time, typically expressed as a time constant (TC). This needs to be optimized based on the amount of damage to the cells.
3. Field strength: This refers to the voltage applied across the electrode gap. This voltage depends on many factors, such as the cuvette gap, cell size, and temperature
4. Buffer: The buffer's resistance, salt concentration, and buffering capacity can all affect electrotransfer efficiency. For example, some sensitive cells prefer a different culture medium composition.
5. Temperature: High power generally favors lower temperatures, such as operating on ice.
6. pH changes: Electrolysis at the electrode can cause pH changes, which can be adjusted using the buffer.
7. Cell number: Overcrowding can cause arcing, while overdense concentrations can reduce the positive rate.
8. Cell quality: Because electrotransfer is inherently damaging to cells, the quality of the cells being electroporated is crucial. Generally, healthy, uncontaminated, actively dividing, and low-passage cells should be selected.
9. Plasmid quality: Poor-quality or contaminated plasmid DNA can reduce electrotransfer efficiency.
Other factors: Moisture, high salt concentrations, and bubbles on the cuvette surface can all cause arcing.
Transient Expression and Stable Integration
Common plasmid transfection methods lack a specific, site-specific integration mechanism. Therefore, when a plasmid is delivered into the cell nucleus, integration occurs randomly, and only a small portion of the plasmid is repaired by DNA breaks during cellular replication and integrated into the host chromosomal genome.
Thus, we summarize several key characteristics:
1.Random integration leads to low integration efficiency, and integration into active transcriptional regions is not always possible;
2.A significant amount of unintegrated plasmid (for example, using 1x10e6 transfection of 5 μg, for a pcDNA3.1 vector plus a 3000bp target gene, approximately 5.37*10e11) The number of copies is gradually diluted or degraded as cells divide.
3.A peak of transient expression typically occurs within 24-96 hours.
4.The integrated copies must undergo antibiotic screening to obtain positive cells, and resistance maintenance is required later.
5.Because integration occurs through DNA break repair and recombination, there is a possibility of further breaks at this site later, potentially disrupting the target gene. Therefore, stability is a challenge. It is recommended to develop a monoclonal stable cell line and perform stability analysis through passage.
6.Linear DNA integrates more efficiently than circular DNA, but it is more difficult to deliver than circular DNA.
7.Different cell types exhibit significant differences, manifesting in both delivery and integration.
8.The delivered plasmid must be free of endotoxins, as endotoxins can cause an immune response.
Stable cell line construction service
Reqbio provides stable cell line development services based on the “Plasmid Electroporation Integration System.” To date, we have successfully generated over 300 stable cell line models, demonstrating extensive experience in electroporation-based genome integration. Please contact us to discuss your project requirements.
Definition
1、Random integration has low integration efficiency and may not necessarily integrate into the transcriptional active regions.
2、Random integration has low integration efficiency and may not necessarily integrate into the transcriptional active regions.
Other stable cell lines
Lentiviral Integration
Flp-FRT Targeted Integration
Random Plasmid Integration
Transposon-Based Integration
If you are interested in ordering, please contact us.
Customer help-line
4008-750-250
sales@reqbio.com
Office address:
3rd Floor, No. 6, Lane 222, Guangdan Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai, China
We Are Pleased to Announce: Global Commercial Licensing Rights for Jurkat E6.1, CHO-K1, and HEK293 Cell Lines Officially Secured.
Explore