
Drug Target Models
GPCR Reporter Cells
Immunotherapy cells
Other Stable Cells
Assay Kits & Reagents
Services
Resources
Company
Professional technology integration to support the entire R&D process
Home>
Company>
Conferences&Events>
【 Good News 】Kebai Biology Reaches New Heights! Honored as a "2024 Jiangsu Province Gazelle Enterprise", shining on the Gazelle list for two consecutive years!
【 Good News 】Kebai Biology Reaches New Heights! Honored as a "2024 Jiangsu Province Gazelle Enterprise", shining on the Gazelle list for two consecutive years!
Background
Since 1975, the global prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled. Obesity has now become a public health issue worldwide. Over the past two decades, in-depth research by the pharmaceutical scientific community into the molecular mechanisms controlling appetite has led to the identification of an increasing number of drug targets related to weight loss. 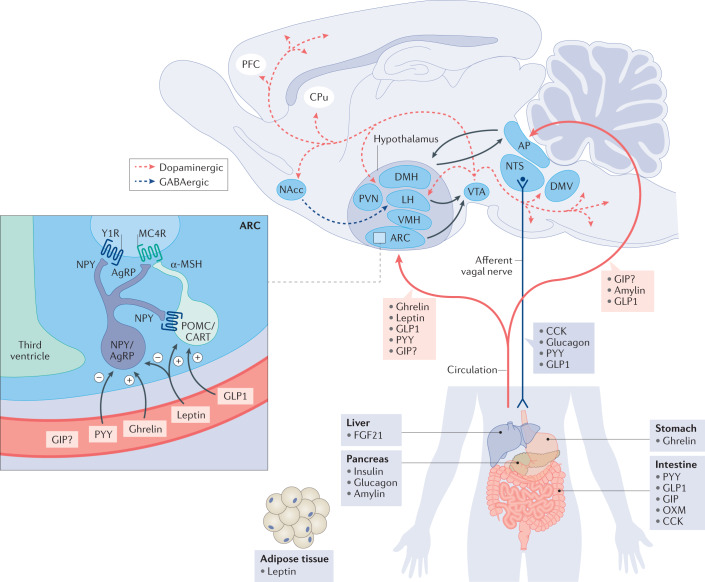
After decades of continuous refinement of their mechanism of action, GLP-1 receptor agonists have shown remarkable success in the weight loss field, bringing excitement to the entire industry and fueling the search for more similar potential targets.
The melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R), a key switch in the central regulation of energy homeostasis in the human body, has a strong foundation of genetic validation, making it one of the ideal targets for weight loss drug development. The successful market launch of Setmelanotide (tradename: Imcivree), an MC4R agonist developed by Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, in 2020, coupled with positive Phase II clinical data for their second-generation oral agent, bivamelagon (an MC4R agonist), in acquired hypothalamic obesity, has reignited interest in MC4R research.
Structure and Function of MC4R
MC4R (Melanocortin-4 Receptor) is a member of the melanocortin receptor family, which belongs to the class A rhodopsin-like G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. Other members include MC1R, MC2R, MC3R, and MC5R. Melanocortin receptors (MC1R-MC5R) are located on various cell types and are distributed across most bodily systems.
MC4R is a crucial component of the central melanocortin system. It is primarily expressed in the paraventricular nucleus (PVH) of the hypothalamus and is a Class A GPCR. Under conditions of high energy balance, pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons release the peptide MC4R agonist, α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH). Binding of α-MSH to MC4R activates MC4R signaling, leading to appetite suppression and reduced food intake. Under conditions of low energy balance, Agouti-related peptide (AgRP) is released in the paraventricular nucleus. AgRP acts as a competitive antagonist of α-MSH binding to MC4R and is also an inverse agonist of MC4R, thereby inhibiting MC4R signaling. 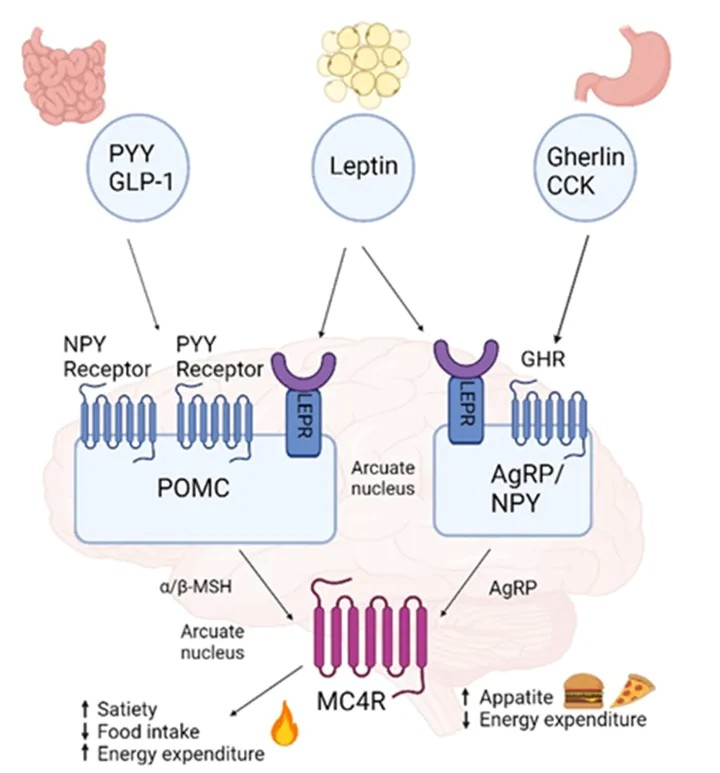
When administered peripherally, Setmelanotide can cross the blood-brain barrier and act on the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and the lateral hypothalamic area, regions involved in appetite regulation. By binding to MC4R, it addresses a missing link in the hypothalamic leptin-melanocortin pathway, consequently suppressing appetite and improving insulin resistance. It also increases resting energy expenditure by shifting substrate oxidation towards fats. 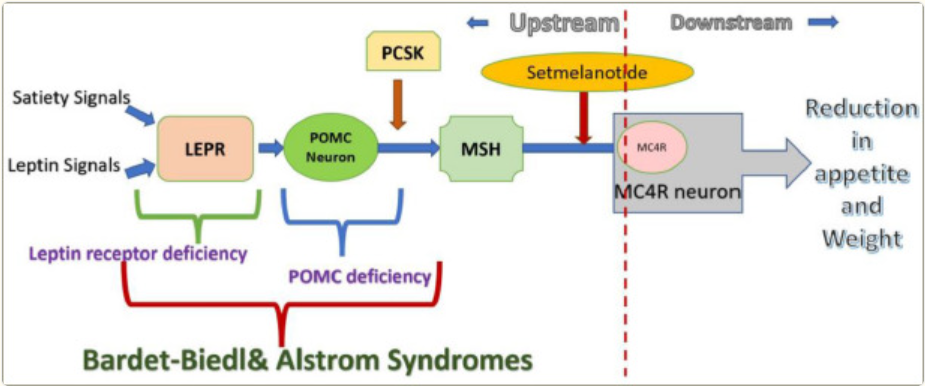
he signaling pathways involving MC4R primarily include the Leptin-Melanocortin pathway, G protein signaling pathways, β-arrestin pathway, and Ca2+ regulatory pathways. These signaling pathways are all associated with obesity and energy metabolism. 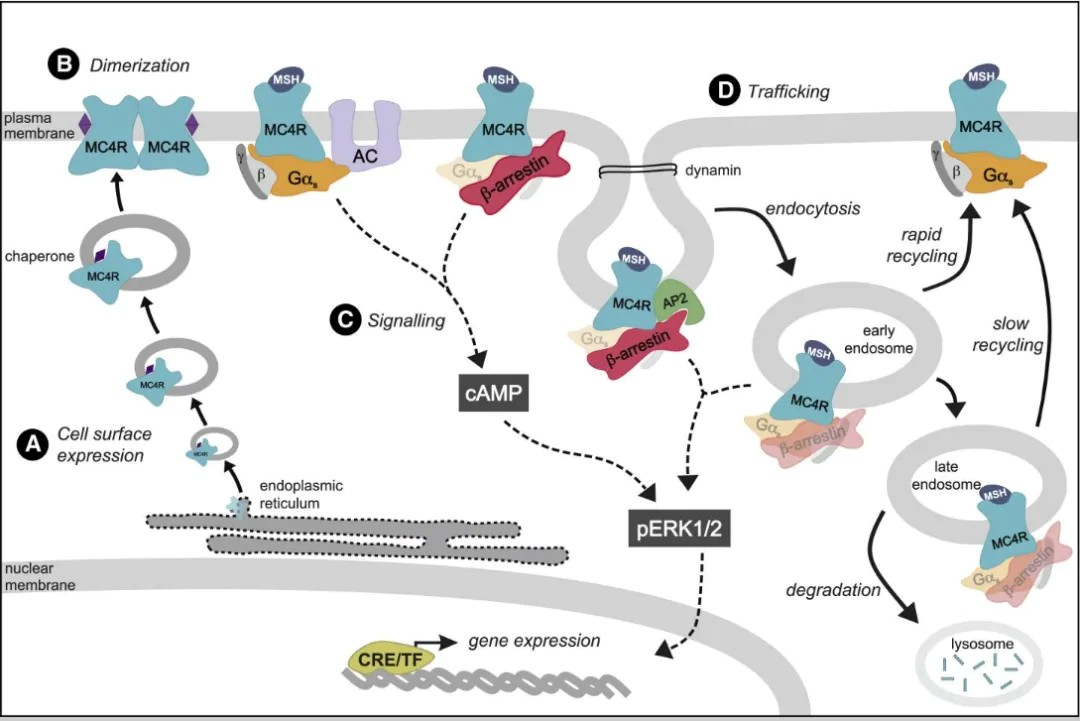
Drug Development Progress
Currently, two MC4R-targeting drugs have been approved globally: Setmelanotide, developed by Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and Bremelanotide, developed by Palatin Technologies in the US. Setmelanotide, approved at the end of 2020, is a single-target MC4R agonist. It had previously received FDA Breakthrough Therapy designation for rare obesities and is approved for treating obesity due to proven deficits in POMC, PCSK1, or LEPR genes, as well as obesity associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. It generated sales revenue of $130 million USD in 2024. Bremelanotide was approved in 2019 for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women. Its weight loss effects were discovered later, representing a case of 'drug repurposing'.
Excluding several drugs that have been terminated or show no recent progress in clinical stages, there are currently multiple MC4R-targeting drugs in clinical and preclinical development, including both small molecules and peptides. Partial information is as follows: 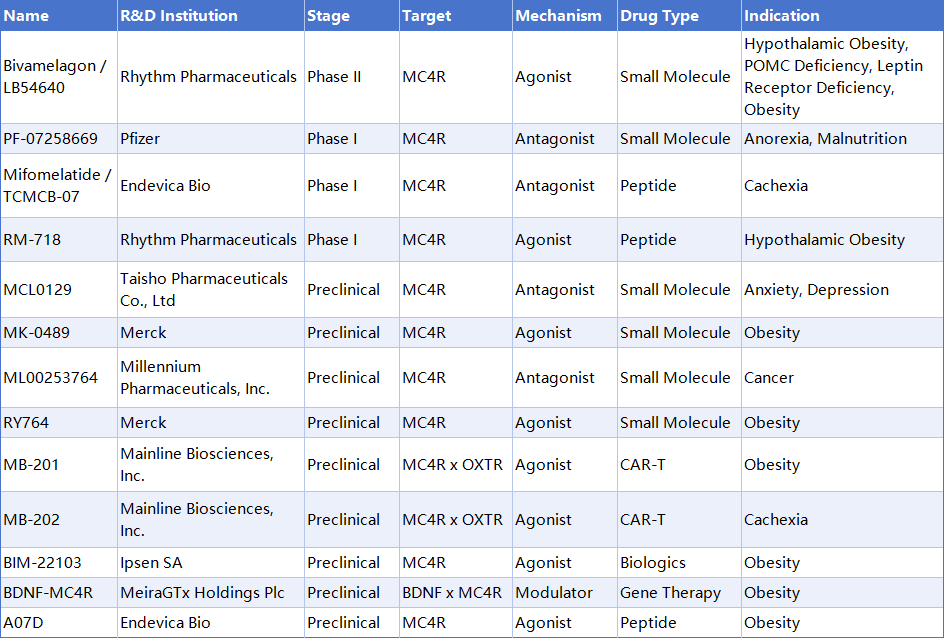
MC4R Cell Models
To support MC4R drug development, Cobetter Bio has developed an MC4R cell model based on the CREB/cAMP signaling pathway for early-stage mechanistic studies of candidate drugs. Results are as follows:
MC4R CHO RQP71547 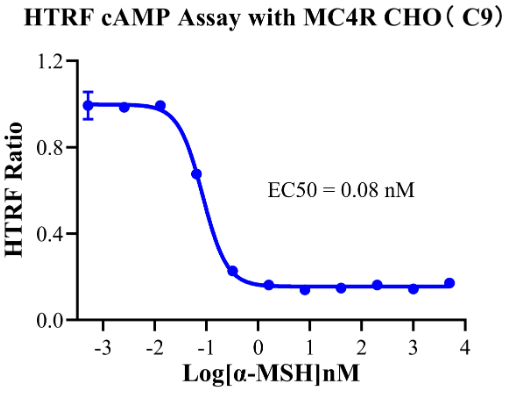
Figure 5:HTRF cAMP Assay with MC4R CHO (C9).
news recommendation
We Are Pleased to Announce: Global Commercial Licensing Rights for Jurkat E6.1, CHO-K1, and HEK293 Cell Lines Officially Secured.
Explore



